Class 10 Hydrocarbon Exercise 18.1 Solutions | Science and Technology Curriculum Development Centre
Disclaimer
The following solutions are contributed by the Sci-Pi community. Each solution that appears on this page has undergone verification by the moderators. However, we highly encourage you to view these solutions as a guide rather than copying everything mentioned here.
2) Write differences between:
Differentiate: Saturated and Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Solution
Differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon are given below:
| Saturated hydrocarbon | Unsaturated hydrocarbon |
|---|---|
| Saturated Hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons having a single bond in between all adjacent carbon atoms. | Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrcarbons having at least one multiple (double or tripple) bond in between two adjacenet carbon atoms. |
| They are comparatively less reactive than unsaturated hydrocarbon. | They are comparatively more reactive than saturated hydrocarbon. |
| Their general formula is \(\rm C_{n}H_{2n + 2} \). | They do not have a general formula. The general formula of alkene is \( \rm C_{n}H_{2n} \) and that of alkyne is \( \rm C_{n}H_{2n - 2} \). |
| Example: alkane. | Example: alkene and alkyne. |
Differentiate: Alkane and alkene
Solution
Differences between alkane and alkene are as follows:
| Alkane | Alkene |
|---|---|
| Alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon that has a single bond between all adjacent carbon atoms. | Alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between two adjacent carbon atoms. |
| Alkane is chemically less reactive. | Alkene is chemicall more reactive. |
| Its general formula is \( \rm C_{n} H_{2n + 2} \). | Its general formula is \( \rm C_{n}H_{2n} \). |
| The suffix for alkane is ‘ane’. | The suffix for alkene is ‘ene’. |
| Example: methane and ethane. | Example: methene and propene. |
Differentiate: Monohydric alcohol and Dihydric alcohol
Solution
Differences between monohydric alcohol and dihydric alcohol are:
| Monohydric Alcohol | Dihydric Alcohol |
| The alcohol having only one (-OH) group in the compound is called monohydric alcohol. | The alcohol having two hydroxyl group(-OH) in one compound is called dihydric alcohol. |
| It is formed by replacing one hydrogen atom of alkane by one hydroxyl group(-OH). | It is formed by the replacement of two hydrogen atoms from alkane by two hydroxyl groups(-OH). |
| They can be represented by a general formula CnH2n+1OH. | They can be represented by a general formula CnH2n(OH)2 |
| For example: Ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) | For example: Ethylene glycol [C2H4(OH)2] |
3) Give reason:
Ethane is known as a saturated hydrocarbon. Why?
Solution
Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are bonded by single covalent bond.
Hence, Ethane(C2H6) is known as a saturated hydrocarbon because its atoms carbon atoms are bonded together by a single covalent bond only.
Glycerol is called a trihydric alcohol. Why?
Solution
The alcohol having three hydroxyl groups(-OH) in one compound is called trihydric alcohol.
Hence, Glycerol [C3H5(OH)3] is called a trihydric alcohol because it has three hydroxyl group(-OH) after the removal of 3 hydrogen atoms from propane. It is the simplest trihydric alcohol.
4) Answer the following questions:
What are hydrocarbons? Write any four examples.
Solution
Hydrocarbons are compounds formed by the covalent bonding between hydrogen and carbon atoms. Generally, they are organic compounds.
Any four examples of hydrocarbons are Methane, Ethane, Propane, and Alcohol.
What do you mean by a saturated hydrocarbon? Write with examples.
Solution
Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are bonded together by a single covalent bond only. Alkanes are known as saturated hydrocarbons.
Some of the examples of saturated hydrocarbons are: Methane, Ethane, Pentane, Heptane etc.
Introduce methane gas along with its two uses.
Solution
Methane:
Methane is a saturated hydrocarbon. It is the simplest and the first member of the alkane series. It is also known as marsh gas because it is found in swamps or marshy land where it is produced by bacterial decomposition of complex vegetables and animal matters.
Molecular formula of methane: CH4
Uses of methane are:
- It is used as a gaseous fuel in industries and household works.
- It is used for making printing ink.
What is alcohol? Write its types on the basis of the hydroxyl group. Also, write their examples along with their molecular formula and the structural formula.
Solution
Alcohol is defined as an organic compound containing hydroxyl group(-OH) attached to a saturated carbon atom or hydrocarbon radical.
On the basis of number of hydroxyl group(-OH) in the molecule of alcohol, it is classified into three types as given below:
1. Monohydric alcohol: The alcohol having only one (-OH) group in the molecule is called monohydric alcohol. Its general formula is ( \(\rm C_{n}H_{2n+1}OH\) ).
Example; methyl alcohol( \(\rm CH_{3}OH\) ). Its structural formula is:

2.Dihydric alcohol: The alcohol having two hydroxyl groups(-OH) in one compound is called dihydric alcohol. Its general formula is ( \(\rm C_{n}H_{2n}(OH)_{2}\) ).
Example; ethylene glycol ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{4}(OH)_{2}\). Its structural formula is:

3. Trihydric alcohol: The alcohol having three hydroxyl groups (-OH) in one compound is called trihydric alcohol. Its general formula is ( \(\rm C_{n}H_{2n-1}(OH)_{3}\) ).
Example; glycerol ( \(\rm C_{3}H_{5}(OH)_{3}\). Its structural formula is:

Write the molecular formula, condensed formula, and the structural formula of the following compounds:
- Ethylene
- Propene
- Acetylene
- Ethyl Alcohol
- Glycerol
Solution
1. Ethylene: Molecular formula: ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{4}\) )
Condensed formula: ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{2}= C_{2}H_{2}\) )
Structural formula:
2. Propene: Molecular formula: ( \(\rm C_{3}H_{6}\) )
Condensed formula: ( \(\rm CH_{2}= CH - CH{3}\) )
Structural formula:

3. Acetylene: Molecular formula: ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{2}\) )
Condensed formula: HC≡CH
Structural formula:
4. Ethyl alcohol: Molecular formula: ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{5}OH\) )
Condensed formula: ( \(\rm CH_{3}-CH{2}-OH\) )
Structural formula:
5. Glycerol : Molecular formula: ( \(\rm C_{3}H_{5} (OH)_{3}\) )
Condensed formula: ( \(\rm CH_{2}OH-CHOH-CH_{2}OH\) )
Structural formula:
Name the alcohol used for the following purposes:
- to make formaldehyde
- used in thermometer
- used as an antiseptic
- to prepare alcoholic beverages
Solution
- to make formaldehyde. Ans: Methyl alcohol
- used in thermometer. Ans: Ethyl alcohol
- used as an antiseptic. Ans: Ethyl alcohol
- to prepare alcoholic beverages. Ans: Ethyl alcohol
Write the structural formula of ethylene. What type of bond is found between hydrogen and carbon? Why is the bond between its carbon atoms weak?
Solution
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is the simplest alkene with the chemical formula ( \(\rm C_{2}H_{4}\) ).The structural formula of ethylene is:
- The bonds between hydrogen and carbon are strong because they share their electrons directly.
- The double bond between carbon atoms is a bit weaker because the atoms are crowded, it has a mix of strong and weak bonds, and the electrons in one part of the bond are spread out instead of being tightly held.
Write any three uses of methane gas.
Solution
Uses of Methane:
- It is used as a gaseous fuel in industries and household works.
- It is used for making printing ink.
- It is used for making carbon black needed for paints and rubber industries.
Write major uses of ethane.
Solution
Major uses of ethane are:
- Ethane is used as a gaseous fuel along with methane.
- It is used for preparing other organic compounds like ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether, etc.
- It is used for making shoe polish.
Write major uses of propane.
Solution
Propane is a type of alkane with molecular formula ( \(\rm C_{3}H_{8}\)).
Major uses of propane are:
- Propane is used as a fuel in lighters and also as a refrigerant.
- It is used to make other type of compounds like glycerol.
- It is used in petroleum industries for cooling purpose.
Define saturated hydrocarbon.
Solution
Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are bonded together by a single covalent bond only.
Define unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Solution
The compounds in which carbon atoms are linked together by multiple bonds(either double or triple covalent bons) are known as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Define alkane.
Solution
An alkane is a type of hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected by single bonds only. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n represents the number of carbon atoms.
Define alkene.
Solution
An alkene is a type of unsaturated hydrocarbon in which the one pair of carbon atoms are bonded by double covalent bonds. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n, where n represents the number of carbon atoms.
Define functional group.
Solution
A functional group is defined as an atom or a group of atoms that define the chemical properties of an organic compound when added to it.
Some examples of functional groups are: Alcohol (-OH), Aldehyde (-CHO), Ether (-O-), etc.
Define homologous series.
Solution
In organic compounds, there exists a series or a group of compounds having the same functional group and similar chemical properties in which each succeeding compound differs from the preceding by -CH2 group or 14 molecular weights. Such a series is known as the homologous series.
In other words, homologous series is defined as a series of organic compounds in which all the organic compounds can be represented by the same general formula and each successive homologue differs from the preceding by a -CH2 group or 16 molecular weight.
Write the molecular formula of the following compounds:
- Glycerol
- Methane
- Ethanol
- Butane
- Propane
- Acetylene
- Ethene
- Ethane
- Propyne
- Methyl Alcohol
Solution
The molecular formulae of the given compounds are:
- Glycerol: $\rm (C_{3}H_{5})(OH)_{3}$
- Methane: $\rm CH_{4}$
- Ethanol: $\rm C_{2} H_{5} OH$
- Butane: $\rm C_{4}H_{10}$
- Propane: $\rm C_{3}H_{8}$
- Acetylene: $\rm C_{2}H_{2}$
- Ethene: $\rm C_{2}H_{4}$
- Ethane: $\rm C_{2}H_{6}$
- Propyne: $\rm C_{3}H_{4}$
- Methyl Alcohol: $\rm CH_{2} OH$
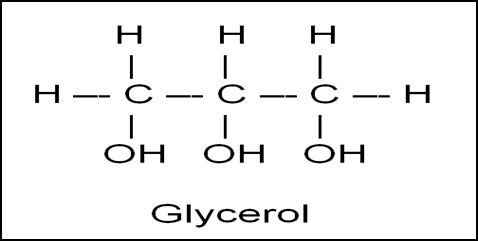
Name the compound formed by the replacement of three hydrogen atoms with three hydroxyl groups (-OH) from propane. Also, write its IUPAC name along with its structural formula. Write its three uses.
Solution
Glycerol is formed by the replacement of three hydrogen atoms with three hydroxyl groups (-OH) making it the simplest trihydric alcohol.
Its IUPAC name is Propane- 1,2,3-triol. Its structural formula is:

Uses of Glycerol:
- Glycerol is used as a sweetening agent in confectionery, beverages and medicines.
- It is used as a lubricant in watches.
- It is used in the preparation of printing inks and stamp pad inks.
Rama has a problem with dry skin on her hands, feet, and face. Which compound can be used to solve her problem? Write the IUPAC name and the structural formula of that compound.
Solution
Glycerol is a alcohol used to manufacture good quality soaps and cosmetics. Hence, Glycerol can be used by Rama to solve her problems.
Additionally, when water is mixed with glycerol, it forms glycerin. Glycerin draws moisture from the environment into the skin, helping to hydrate and improve its appearance. This can solve the problem with dry skin on her hands, feet, and face.
The IUPAC name of glycerol is propane-1,2,3-triol.
Its structural formula is:
About the Textbook